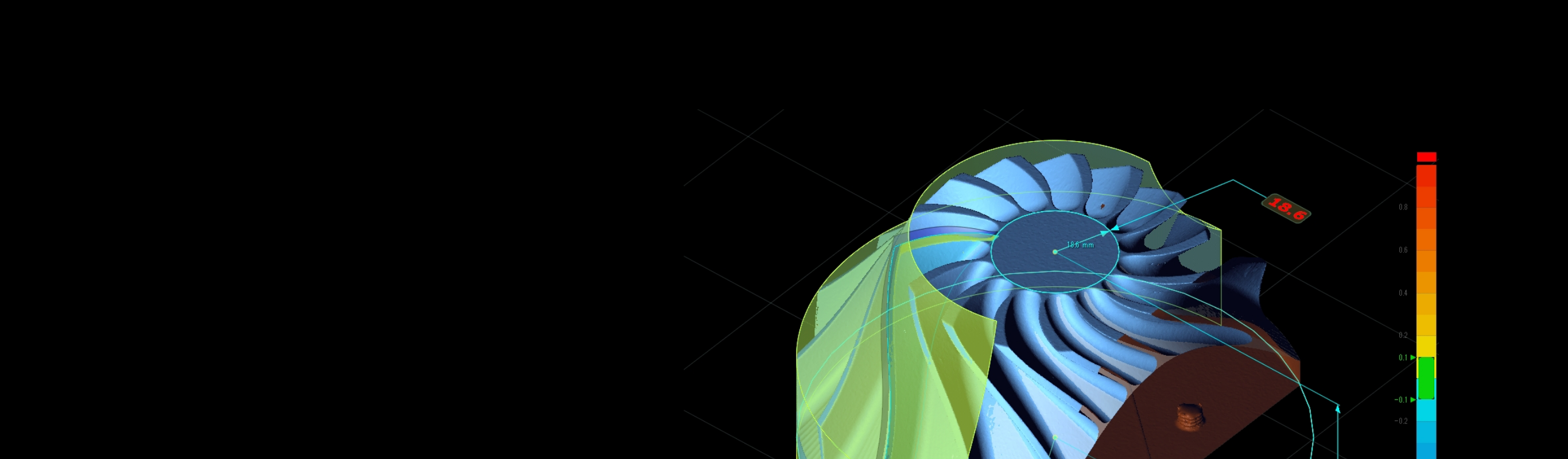

Reverse Engineering
A viable method of creating a virtual model of an existing part. Reverse engineering is the art of recreating the original design of a component.
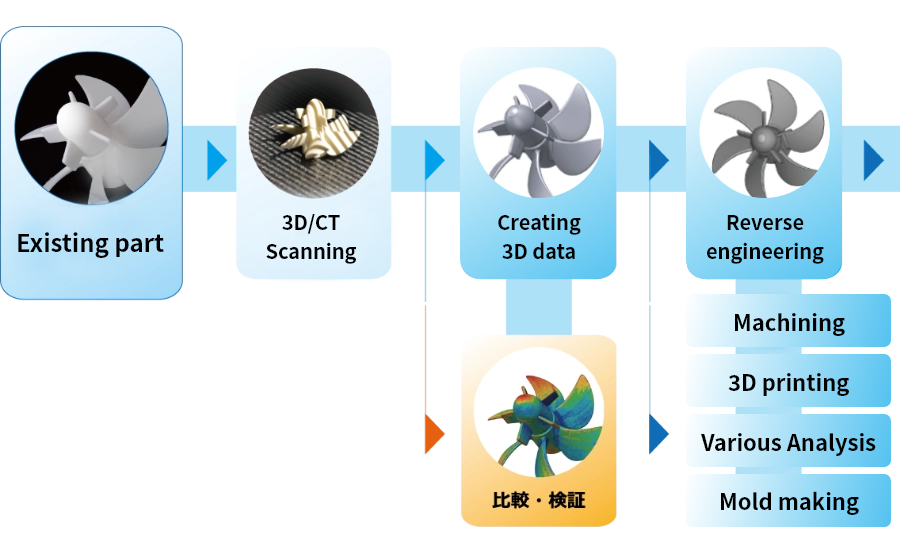
Note:Data at any stage can be provided upon request.
(We also accept data construction from the provision of scan data)
From development to design, prototyping, and mass production, Yasojima Proceed aims to provide services that are useful to customers in all processes of product development.
- Reverse engineering based on scan data.
- In-house prototyping by 3D Printing.
- Specifying areas which may require design modification, by comparing and verifying 3D CAD data with actual product scan data.
Yasojima Proceed’s total service meets all your 3D printing needs. Leave it up to the experts to ensure you get the most benefit from this versatile technology.
Yasojima Proceed’s reverse engineering experts will answer paramount questions in determining the successful path of data output.
As it can speed up development and cut production costs, reverse engineering is paramount to multiple industries such as manufacturing, automotive, aerospace, and in a wider sense, even areas such as medical. With the tools and vast experience necessary to provide reverse engineering services for many different components, parts, and assemblies, Yasojima Proceed can streamline your project.
Data variations
| 3D model | Surface unevenness | Error with measured data | Advantages & disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
STL/Voxel data 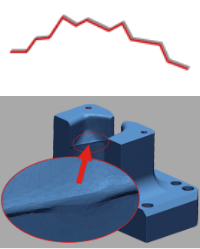
| Most | Less |
|
Generated surface automatically using point cloud 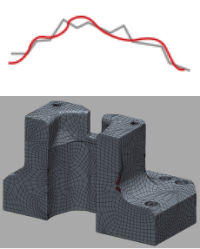
| Many | Medium |
|
Surface data using point cloud 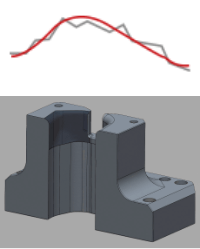
| Medium | Big |
|
Surface data referred to point cloud 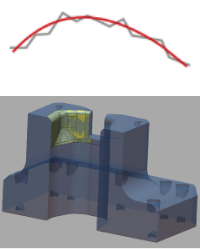
| Less | Big |
|
In reverse engineering, the method of creating surface data may change depending on the location even for the same part. In doing so, we will interweave the above methods to create surfaces in a composite manner.